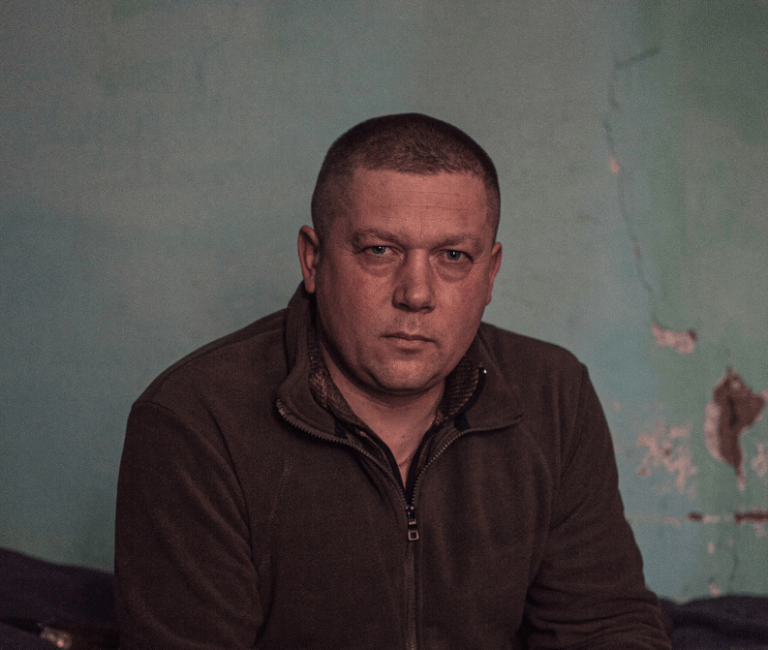
Photo: Un commandant de bataillon de la 46e brigade d’assaut aérien, surnommé Kupol, dans un lieu tenu secret dans l’est de l’Ukraine le 4 mars. Ce homme a perdu tous les 600 hommes de son bataillon
(Photo par Alice Martins pour le Washington Post)
La qualité de la force militaire ukrainienne, présentée par certains réseaux occidentaux comme un avantage substantiel sur la Russie, a été fortement dégradée par une année de lourdes pertes qui ont éloigné du champ de bataille bon nombre des combattants les plus expérimentés, blessé ou tués. Ce qui a conduit certains responsables ukrainiens à remettre en question la capacité de Kiev à monter une offensive au printemps prochain comme l’an dernier.
L’armée ukrainienne ne divulgue pas le nombre de ses victimes, même à ses plus fervents partisans occidentaux, mais sur le front, il y a un sentiment de pessimisme palpable alors que les commandants ont du mal à former de nouvelles recrues et disent que les armes n’arrivent pas assez vite.
L’Article du Washington post en Anglais
Ukraine short of skilled troops and munitions as losses, pessimism grow
By Isabelle Khurshudyan, Paul Sonne and Karen DeYoung
Soldiers train at a firing range at an undisclosed location in eastern Ukraine on March 4. (Alice Martins for The Washington Post)
Listen
13 min
Comment
2986
Gift Article
Share
DNIPROPETROVSK REGION, Ukraine — The quality of Ukraine’s military force, once considered a substantial advantage over Russia, has been degraded by a year of casualties that have taken many of the most experienced fighters off the battlefield, leading some Ukrainian officials to question Kyiv’s readiness to mount a much-anticipated spring offensive.
Are you on Telegram? Subscribe to our channel for the latest updates on Russia’s war in Ukraine.
U.S. and European officials have estimated that as many as 120,000 Ukrainian soldiers have been killed or wounded since the start of Russia’s invasion early last year, compared with about 200,000 on the Russian side, which has a much larger military and roughly triple the population from which to draw conscripts. Ukraine keeps its running casualty numbers secret, even from its staunchest Western supporters.
Statistics aside, an influx of inexperienced draftees, brought in to plug the losses, has changed the profile of the Ukrainian force, which is also suffering from basic shortages of ammunition, including artillery shells and mortar bombs, according to military personnel in the field.
“The most valuable thing in war is combat experience,” said a battalion commander in the 46th Air Assault Brigade, who is being identified only by his call sign, Kupol, in keeping with Ukrainian military protocol. “A soldier who has survived six months of combat and a soldier who came from a firing range are two different soldiers. It’s heaven and earth.”
“And there are only a few soldiers with combat experience,” Kupol added. “Unfortunately, they are all already dead or wounded.”
Such grim assessments have spread a palpable, if mostly unspoken, pessimism from the front lines to the corridors of power in Kyiv, the capital. An inability by Ukraine to execute a much-hyped counteroffensive would fuel new criticism that the United States and its European allies waited too long, until the force had already deteriorated, to deepen training programs and provide armored fighting vehicles, including Bradleys and Leopard battle tanks.
The situation on the battlefield now may not reflect a full picture of Ukraine’s forces, because Kyiv is training troops for the coming counteroffensive separately and deliberately holding them back from current fighting, including the defense of Bakhmut, a U.S. official said, speaking on the condition of anonymity to be candid.
Ukraine holds the line in brutal battle for Bakhmut
2:27
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky said on Mar. 6 that he intends to hold the line in Bakhmut, as the brutal battle for the eastern city continues. (Video: Reuters)
Andriy Yermak, head of Ukraine’s presidential office, said the state of the Ukrainian force does not diminish his optimism about a coming counteroffensive. “I don’t think we’ve exhausted our potential,” Yermak said. “I think that in any war, there comes a time when you have to prepare new personnel, which is what is happening right now.”
And the situation for Russia may be worse. During a NATO meeting last month, U.K. Defense Minister Ben Wallace said that 97 percent of Russia’s army was already deployed in Ukraine and that Moscow was suffering “First World War levels of attrition.”
Kupol said he was speaking out in hopes of securing better training for Ukrainian forces from Washington and that he hopes Ukrainian troops being held back for a coming counteroffensive will have more success than the inexperienced soldiers now manning the front under his command.
“There’s always belief in a miracle,” he said. “Either it will be a massacre and corpses or it’s going to be a professional counteroffensive. There are two options. There will be a counteroffensive either way.”
A battalion commander in the 46th Air Assault Brigade, who goes by the call sign Kupol, in an undisclosed location in eastern Ukraine on March 4. (Alice Martins for The Washington Post)
How much increased Western military aid and training will tip the balance in such a spring offensive remains uncertain, given the scars of attrition that are beginning to show.
One senior Ukrainian government official, who spoke on the condition of anonymity to be candid, called the number of tanks promised by the West a “symbolic” amount. Others privately voiced pessimism that promised supplies would even reach the battlefield in time.
“If you have more resources, you more actively attack,” the senior official said. “If you have fewer resources, you defend more. We’re going to defend. That’s why if you ask me personally, I don’t believe in a big counteroffensive for us. I’d like to believe in it, but I’m looking at the resources and asking, ‘With what?’ Maybe we’ll have some localized breakthroughs.”
“We don’t have the people or weapons,” the senior official added. “And you know the ratio: When you’re on the offensive, you lose twice or three times as many people. We can’t afford to lose that many people.”
Such analysis is far less optimistic than the public statements by Ukraine’s political and military leadership.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has described 2023 as “the year of victory” for Ukraine. His military intelligence chief, Kyrylo Budanov, touted the possibility of Ukrainians vacationing this summer in Crimea, the peninsula Russia annexed illegally from Ukraine nine years ago.
“Our president inspires us to win,” Col. Gen. Oleksandr Syrsky, Ukraine’s ground forces commander, said in an interview with The Washington Post. “Generally, we all think the same, and we understand that for us it is of course necessary to win by the end of the year. And it is real. It is real if we are given all the help which we have been promised by our partners.”
On the front lines, however, the mood is dark.
Kupol, who consented to having his photograph taken and said he understood he could face personal blowback for giving a frank assessment, described going to battle with newly drafted soldiers who had never thrown a grenade, who readily abandoned their positions under fire and who lacked confidence in handling firearms.
Soldiers train at a firing range in an undisclosed location in eastern Ukraine on March 4. (Alice Martins for The Washington Post)
His unit withdrew from Soledar in eastern Ukraine in the winter after being surrounded by Russian forces who later captured the city. Kupol recalled how hundreds of Ukrainian soldiers in units fighting alongside his battalion simply abandoned their positions, even as fighters for Russia’s Wagner mercenary group pressed ahead.
After a year of war, Kupol, a lieutenant colonel, said his battalion is unrecognizable. Of about 500 soldiers, roughly 100 were killed in action and another 400 wounded, leading to complete turnover. Kupol said he was the sole military professional in the battalion, and he described the struggle of leading a unit composed entirely of inexperienced troops.
“I get 100 new soldiers,” Kupol said. “They don’t give me any time to prepare them. They say, ‘Take them into the battle.’ They just drop everything and run. That’s it. Do you understand why? Because the soldier doesn’t shoot. I ask him why, and he says, ‘I’m afraid of the sound of the shot.’ And for some reason, he has never thrown a grenade. … We need NATO instructors in all our training centers, and our instructors need to be sent over there into the trenches. Because they failed in their task.”
He described severe ammunition shortages, including a lack of simple mortar bombs and grenades for U.S.-made MK 19s.
Ukraine has also faced an acute shortage of artillery shells, which Washington and its allies have scrambled to address, with discussions about how to shore up Ukrainian stocks dominating daily meetings on the war at the White House National Security Council. Washington’s efforts have kept Ukraine fighting, but use rates are very high, and scarcity persists.






Commentaires Facebook